Spoofing with AUUD: A Deep Dive into Market Manipulation

There is demand. There is no demand. Where’s that selling pressure gone in a few minutes? Ever feel like the stock market is playing tricks on you? Well, sometimes it is. Say thanks to a manipulative tactic called spoofing! It is an illegal trading strategy where traders place large fake orders to fool others into thinking the market is moving in a certain direction.
If you trade in volatile or smaller-cap stocks, understanding how spoofers manipulate prices is important to stay ahead of the game. In this article, you’ll learn what spoofing is, how it works step by step, and why it’s such a powerful form of manipulation.
To clarify, we will share some real-world examples, like how Auddia Inc. (AUUD) became a target for spoofers. You’ll also explore key tools and techniques to detect spoofing, such as order flow analysis and spotting volume discrepancies. Moreover, we will also give you certain red flags that can help you detect the presence of spoofing. Let’s begin.
What is Spoofing? A Brief Overview
Spoofing is a manipulative trading strategy where traders place large orders to create fake buy or sell signals. These orders give the appearance of significant supply or demand but are canceled before they can be executed. The primary intent behind this practice is to trick other traders into thinking that the market is moving in a particular direction, prompting them to react. Once the market shifts in the desired direction, spoofers cancel their orders, causing confusion and market misdirection.
Want to better understand the meaning of spoofing in trading? Read our exclusive article: What is Spoofing Trading?
How does Spoofing in Trading Work?
Let’s understand in simple steps:
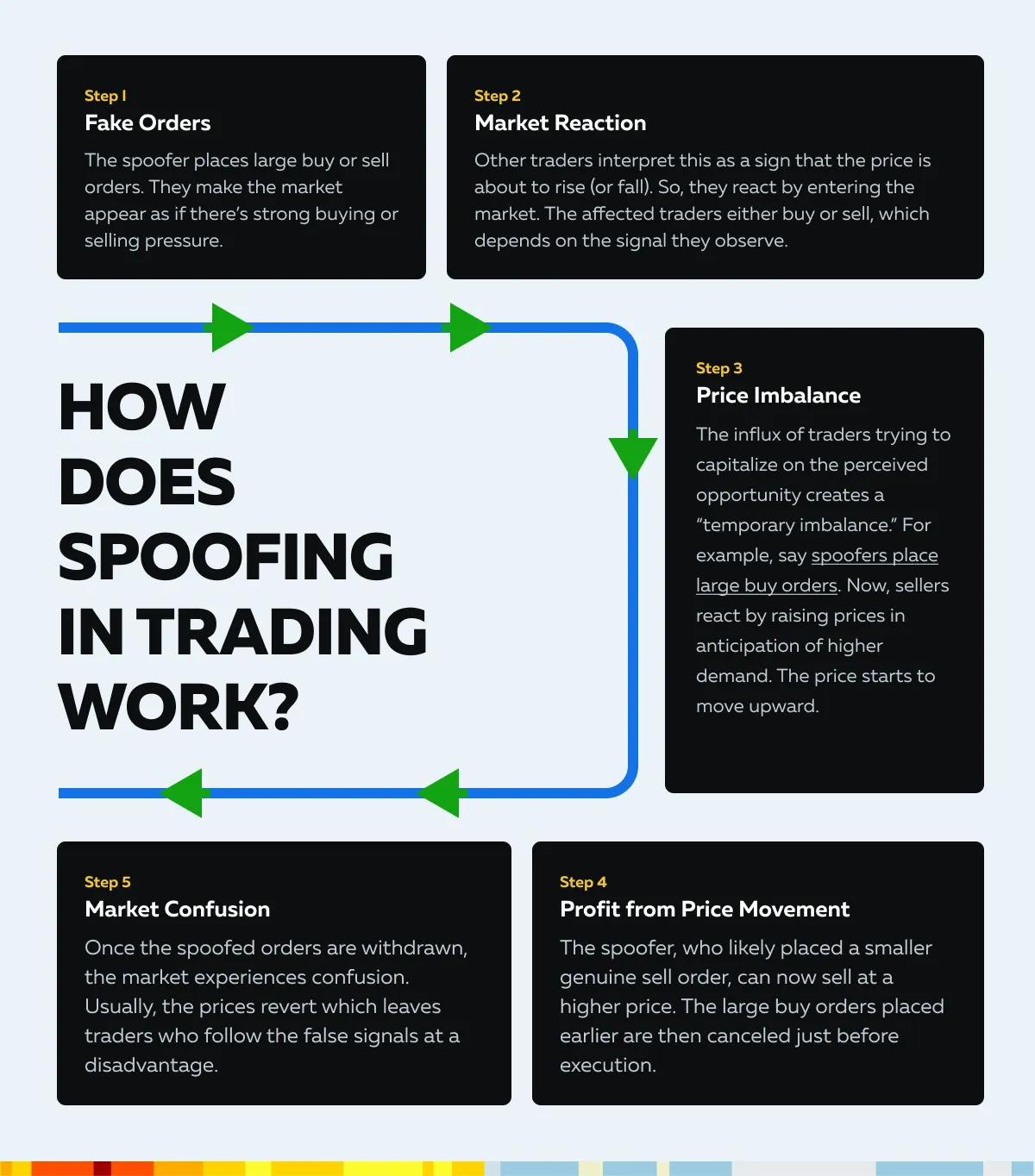
Why Spoofing is a Strong Manipulative Technique?
It is worth mentioning that often spoofers have access to significant liquidity. This gives their fake orders more weight in influencing market prices. Also, this strategy exploits the psychology of other traders. By creating an illusion of strong buying or selling pressure, it triggers fear or greed and pushes traders to make hasty decisions. In most cases, spoofing in trading causes short-term market imbalances. It creates price fluctuations that benefit the spoofer’s real position.
Spoofing + Layering = Big Market Manipulation
Most spoofers often use a technique called “layering.” Here they place large orders at various price levels. This placement exaggerates the appearance of strong buying or selling interest. By layering these orders, it looks like there’s significant activity across different price points.
It is worth mentioning that the main aim of layering is to create the illusion of market momentum. This momentum tricks traders into reacting based on false market signals. Once the price shifts in the intended direction, the spoofer withdraws all the deceptive orders.
Learn how to detect market manipulation with our real-time tools at Bookmap. Get started here!
What are the Legal Consequences?
Spoofing in trading is illegal in many regulated markets due to its manipulative nature. Regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) have taken serious actions against spoofing. Historically, they have imposed heavy fines and criminal charges.
Some notable cases are related to:
- “Navinder Singh Sarao,” who was accused of contributing to the 2010 Flash Crash through spoofing.
- “JP Morgan,” where traders were fined billions for manipulating the precious metals market using spoofing tactics.
Case Study: Spoofing in Trading with AUUD Stock

Auddia Inc. (AUUD) is a technology company. It is focused on developing AI-powered audio content platforms. The primary product of the company offers a commercial-free listening experience for radio and allows users to access content seamlessly. Like many smaller-cap stocks, AUUD has experienced significant volatility due to its relatively low:
- Market capitalization,
and
- Trading volume.
It must be noted that generally smaller-cap stocks are more prone to price manipulation. This happens because even a few large orders can significantly affect the price. Consequently, AUUD became a target for manipulative strategies like spoofing. Now, let’s see how it happened:
The Spoofing Incident
In March 2021, AUUD experienced a sudden price drop due to large sell orders being placed in the market. These sell orders created the impression that there was a lot of selling pressure on the stock. As a result, traders panic and rushed to sell their shares. They thought that the price was about to fall further.
However, these large sell orders were not real. They were canceled before they could even be executed. It was a case of spoofing where fake sell orders successfully manipulated the market into thinking there was excess supply. Eventually, this prompted a sell-off.
Protect yourself from spoofing in the market by using our advanced analytics at Bookmap. Join now!
Market Reaction
Once the large spoofed orders were withdrawn, AUUD’s stock price rebounded sharply. This sudden recovery indicated that:
- The initial sell-off was based on false signals,
and
- Real buying demand re-emerged.
Unfortunately, many retail traders who had reacted to the fake orders by selling at lower prices faced losses. These traders believed the stock was about to experience a steep decline, so they sold in a panic, only to see the price recover once the fake orders were canceled. The manipulators, however, had already gained from the artificially created price movement.
Key Takeaway
This case with AUUD is a clear example of how spoofing can create temporary price distortions in the market. Spoofers gain an unfair advantage by:
- Manipulating market sentiment,
and
- Fooling retail traders into making hasty decisions (that too based on false information).
As a result, retail traders often suffer losses when they react to these fabricated signals.
Detecting Spoofing in AUUD: Tools & Indicators

To identify spoofing activity in stocks such as AUUD, traders can use several techniques like order book analysis and assessing volume spikes. Using these methods, traders can easily track unusual order patterns and cancellations before execution. Let’s understand in detail:
- A) Order Flow Analysis
Order flow analysis allows traders to monitor the movement of buy and sell orders. This assessment helps to identify unusual activity. In the case of spoofing, large orders often appear out of place and don’t match the typical order sizes seen for a stock like AUUD. These large orders are a red flag for spoofing and can be caught via thorough order flow analysis.
Let’s understand better through an example:
- Say the average sell order size of AUDD is around 1,000 shares.
- Suddenly, multiple orders of 50,000 shares each are placed.
This suggests unusual behavior. These orders create the illusion of massive selling pressure and prompt other traders to react.
- Next, a trader places 50,000 shares at a key price level.
- However, they cancel within seconds or milliseconds before the market reaches that price.
This clearly shows that these orders were likely meant to mislead the market.
Additionally, you can also make an order size and speed comparison. The size and speed of these large orders compared to the average flow also help in detecting spoofing. For example, on average, AUUD trades about 100 orders per minute, each around 1,000 shares. But suddenly, the number jumps to 200 orders with each being 50,000 shares, followed by rapid cancellations. This is a strong sign of spoofing.
Identify market manipulation and stay ahead with real-time data analysis using our advanced tools at Bookmap. Sign up today!
Another technique to detect spoofing is checking for “volume discrepancies.” These usually occur when the size of buy or sell orders does not align with normal market behavior. This is particularly suspicious if the market shows unusually large orders that never result in actual trades.
For example:
- A trader notices a significant number of large sell orders in the order book.
- However, none of them get executed.
- Instead, they are canceled just before execution.
- This creates false supply-demand signals.
- Also, it makes the stock look like it’s about to experience a significant move.
In such cases, analyzing the order book for patterns where large orders are placed but do not follow through with trades can help traders detect potential spoofing. In smaller-cap stocks like AUUD, where volatility is high, such large unexecuted orders can significantly impact the stock price. Here’s why:
- Smaller-cap stocks often have fewer buyers and sellers.
- When a spoofer places a large sell or buy order without intending to execute it, it creates the illusion of increased supply or demand.
- Because there’s less liquidity in smaller-cap stocks, these large orders have a stronger influence on traders’ perceptions.
- This easily means that the price will drop (in the case of a large sell order) or rise (in the case of a large buy order).
- This effect is amplified in volatile stocks.
Red Flags to Watch Out For
One of the most obvious signs of spoofing is large orders that appear at critical price points (like support or resistance levels) but never execute. These orders show up briefly and influence the decisions of traders to cancel quickly before any actual trades occur.
Apart from this, you can also check for these red flags:
| Rapid Fluctuations in Buy/Sell Walls | Aggressive Orders That Vanish |
|
|
How to Confirm Moves with Volume?
To differentiate between legitimate market moves and spoofing, traders should always check for actual volume behind the order flow. If large orders are causing a significant price spike or drop but aren’t accompanied by meaningful trade volume, this could indicate that the movement is artificial.
Real trades generate consistent volume, whereas spoofed orders manipulate prices without real transaction activity.
Conclusion
Spoofing is a deceptive and manipulative trading strategy that creates false signals in the market and leads to price distortions. It causes significant financial harm, especially to retail traders who unknowingly react to these fake orders. By placing large buy or sell orders and canceling them before execution, spoofers create confusion and prompt other traders to make hasty decisions based on misleading market signals moreover, spoofing results in sharp price movements that don’t reflect real market demand or supply.
Therefore, detecting spoofing is important to protect yourself from its effects. To make an early detection, you can use our advanced market analysis tool “Bookmap.” It offers several modern features such as liquidity heatmaps, order flow analysis, and real-time data tracking. Using these, you can easily spot unusual activity and even confirm if there is real volume behind price movements. Wish to stay ahead of market manipulators? Join our Bookmap today!
 Twitter
Twitter
 Facebook
Facebook