Market Profile Trading: Understanding its Power and Impact

Market Profile Trading is more than just another tool in financial analysis; it’s a game-changer. From a unique approach to understanding markets, it’s now a must-know for top traders.
In this guide, we’ll break down the essentials of Market Profile, explore how traders use it in real-world situations, and even see its power in action in the Blue Jacket competition. Ready to dive deep and level up your trading? Let’s get started.
What is Market Profile Trading?
Market profile trading examines financial markets by offering a unique perspective on market behavior. It focuses on the relationship between price, volume, and time.
It provides traders and investors with insights into the market’s:
Structure
Price distribution, and
Trading activity happening over a specific period.
Developed by J. Peter Steidlmayer in the 1980s, Market profile trading has since gained popularity among both institutional and retail traders for its ability to offer a deeper understanding of market dynamics.
Market profile trading organizes price and volume data in a graphical format called a “market profile chart,” which displays the market’s price distribution over time. This chart helps traders identify areas of strong and weak demand, as well as potential price levels where significant trading activity is concentrated.
The Three Building Blocks of Market Profile Trading
Market profile trading is a methodology that focuses on three fundamental building blocks or elements, which are:
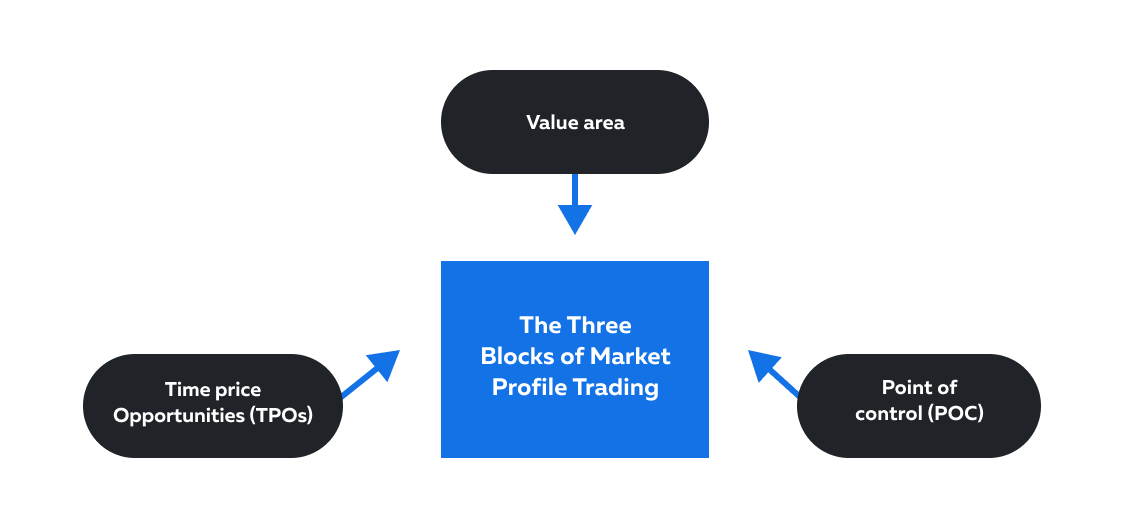
| The Element: | What does it represent? | Practical Use: | What insights do traders gain? |
| Time Price Opportunities (TPOs) | TPOs are vertical bars, or “brackets” that represent a specific price range traded during a given period. | A cluster of TPOs around a particular price level indicates that traders are actively participating and transacting at that level. | This information helps traders identify:
a) Potential support and resistance levels, b) Entry and exit points, and c) Areas of price consolidation
|
| Value Area | It represents the price range within which approximately 70% of the trading volume occurred during a specified period. | If the current price moves outside the Value Area, it signals a potential trend continuation or reversal. | This information helps traders to spot emerging trends. |
| Point of Control (POC) | The point of control refers to the price level at which the highest volume of trading activity occurred during a specific period. | Case 1: If the POC is located near a support or resistance level, it can serve as a confirmation of the level’s significance.
Case 2: If the market moves away from the POC, traders might anticipate a potential trend in the direction of the movement. | Traders use the POC to identify levels of equilibrium between buyers and sellers. |
Must Read: Traders often merge data from TPOs, Value Area, and POC for comprehensive insights. For instance, if TPOs highlight accumulation near a pivotal support level inside the Value Area, and the POC corroborates high activity at the same level, traders might see this as a robust support zone, favoring long trades.
Volume Profile vs. Market Profile: Distinguishing the Two
Volume Profile and Market Profile, though often used interchangeably, have distinct methodologies in market analysis. Here’s a breakdown of both profiles:

Volume Profile:
- This approach focuses primarily on the vertical representation of trading volume at various price levels.
- It provides insights into areas of high and low trading activity and helps identify support and resistance levels.
- Volume Profile does not place as much emphasis on time-based analysis as Market Profile does.
Market Profile:
- Integrates both price and time, constructing TPOs to represent traded price ranges over specific intervals.
- Delivers a holistic understanding of market dynamics by mapping the relationship between price levels, volume, and time.
- Distinguishes itself through its time-centric approach, providing traders with a deeper insight into market structure.
For a clearer distinction, refer to the comparative table below:
Parameters | Volume Profile | Market Profile |
Focus | Primarily on trading volume | Focuses on price, time, and volume |
Representation | Vertical histogram | TPOs (vertical bars) |
Information | Shows volume at specific price levels | Depicts price ranges and time spent trading within those ranges |
Time Consideration | Less emphasis on time | Emphasizes time-based analysis |
Key Components | Volume at price levels (PVP, VAH, VAL) | TPOs, Value Area, Point of Control |
Interpretation | Identifies areas of high/low trading activity | Detects support/resistance levels, trend shifts, and gauges market sentiment |
Application | Effective for spotting support/ resistance levels and potential breakout zones | A comprehensive view of market dynamics, trend confirmation, and strategic trade setups |
Market Profile Trading Strategies
Market Profile Trading offers various strategies that cater to different market conditions, helping traders refine their decisions and improve outcomes. Here are some common strategies used by traders:
1. Value Area Trading
- Traders use the Value Area (where 70% of the trading volume occurs) to determine potential trading opportunities.
- Strategy: When the price re-enters the Value Area after breaking out, it often signals a potential reversal. Traders can use this information to plan long or short trades.
2. Support and Resistance Plays
- Identifying support and resistance levels from the Value Area boundaries or the Point of Control (POC) is a common strategy.
- Strategy: Traders might look for rejection at these levels, which could signal potential entry points with tight stop-losses.
3. Trend Following
- By observing the Value Area shifting higher or lower over time, traders can identify and confirm trends.
- Strategy: Enter trades in the direction of the trend, using the POC and TPO clusters for confirmation.
4. Breakout Trading
- Market Profile charts often reveal periods of consolidation followed by breakouts.
- Strategy: Traders monitor price action near the Value Area extremes. If the price breaks out and sustains above or below the extremes, it may signal a new trend.
By combining these strategies with other technical indicators, traders can increase their odds of success and better manage risks in dynamic market environments.
How Does Market Profile Trading Guide Trading Decisions?
Market profile trading guides trading decisions by providing traders with valuable insights into market trends, risk management, and market sentiment. Here’s how traders use market profile to make informed choices:

Identifying Market Trends:
- Market Profile helps traders identify market trends by visually representing the distribution of trading activity and price levels.
- By observing the shape of the market profile chart, traders can interpret whether the market is in a trending phase, a consolidation phase, or a reversal.
- For example,
- In an up-trending market, the Value Area might be shifting higher, indicating higher demand and potential upward momentum.
- Conversely, a market profile with a wider range and more balanced distribution may indicate a consolidation phase.
Managing Risk:
- Market Profile aids in risk management by highlighting key support and resistance levels, as well as areas of high trading activity.
- Traders can use the value area and point of control to identify levels where the price is likely to find support or encounter resistance.
- This information can be crucial for setting stop-loss orders and profit targets.
Spot Market Sentiment:
- Market Profile provides insights into market sentiment by showing where most of the trading activity is concentrated.
- For example,
- If the point of control is positioned near the upper end of the Value Area, it suggests bullish sentiment.
- On the other hand, if the point of control is closer to the lower end of the Value Area, it may indicate bearish sentiment.
Additionally, observing the shape of the TPOs can also indicate whether the majority of traders are buying or selling at specific price levels, helping traders fine-tune their strategies based on prevailing market sentiments.
Market Profile Charts
A Market Profile Chart is the cornerstone of Market Profile Trading, visually representing the distribution of trading activity across price and time. Understanding its components is essential for leveraging its full potential.
Key Features of Market Profile Charts:
- Time Price Opportunities (TPOs):
- Represented by letters or brackets, TPOs display price levels traded during specific time intervals.
- A dense cluster of TPOs indicates significant market activity at that price.
- Value Area:
- The Value Area highlights the price range where most of the trading volume occurred.
- It serves as a benchmark for identifying support, resistance, and potential breakout zones.
- Point of Control (POC):
- The POC is the price level with the highest trading activity.
- It acts as a balance point, often indicating equilibrium between buyers and sellers.
How to Interpret Market Profile Charts:
- Trending Markets: A progressive shift in the Value Area and POC indicates a trending market.
- Consolidation Phases: A balanced profile with TPOs concentrated in the middle signals consolidation.
- Breakouts: Price movement away from the Value Area extremes often leads to breakouts, creating trading opportunities.
Benefits of Market Profile Charts:
- Enhanced Market Understanding: Gain insights into market structure and dynamics.
- Precision in Trade Entries and Exits: Use key levels such as the Value Area and POC to refine decisions.
- Improved Risk Management: Set more accurate stop-loss and profit targets by analyzing trading volume and price distribution.
Market Profile Charts provide a structured and intuitive way for traders to interpret complex market data, offering a significant edge in both day-to-day trading and competitive environments.
Practical Applications of Market Profile Trading
Traders use market profile trading to identify strategic trade setups like:
- Poor Highs/Lows,
- Determine support and Resistance levels
- Differentiate between consolidation and breakout periods, and
- Confirm trends
By incorporating these insights into their trading decisions, traders aim to enhance decision-making and increase their probabilities of success. Here are some practical applications of market profile trading:
1. Strategic Trade Setups:
- Traders use Market Profiles to devise strategic trade setups based on the insights gained from the distribution of trading activity.
- For example,
- A trader might identify a “Poor High” or “Poor Low” formation on the market profile chart.
- This occurs when the market makes a brief excursion beyond the previous day’s high or low but fails to sustain that level and returns within the Value Area.
- This setup could signal a potential reversal, prompting the trader to enter a trade with the expectation that the market will reverse its direction.
2. Support and Resistance Levels:
- Market Profile helps traders identify support and resistance levels with greater precision.
- Additionally, the upper and lower boundaries of the value area serve as potential areas where prices might reverse.
- By aligning these levels with other technical indicators, traders can make more informed decisions about placing stop-loss and take-profit orders.
3. Periods of Consolidation and Breakout:
Market profile assists traders in distinguishing between periods of consolidation and potential breakout scenarios in the following manner:
Aspects | Consolidation | Breakout Opportunities |
Indicator | During consolidation, the Value Area narrows, reflecting a lack of directional movement. | If the market profile shows a wide Value Area with price acceptance at the extremes, it suggests potential breakout opportunities.
|
Trader’s Action | Traders consider range-bound strategies, such as mean reversion techniques, within these periods. | Traders can prepare for breakout trades by monitoring the price’s reaction as it approaches the Value Area boundaries. |
4. Trend Identification and Confirmation:
- Traders utilize market profiles to confirm or identify emerging trends.
- If the market profile consistently shows a one-sided distribution of TPOs and the point of control shifts in the direction of the trend, it suggests a strong and sustained trend.
The Competitive Advantage: Market Profile in Trading Competitions
In the world of trading competitions, having a deep understanding of tools like the Market Profile can provide participants with an unparalleled edge. For instance, in one of the Blue Jacket competitions, a participant showcased their proficiency with Market Profile by analyzing the intricate relationship between price, time, and volume. View insights into market profile here.

They then presented a meticulous trading strategy backed by insightful screenshots and videos, explaining their moves every step of the way. This strategy not only highlighted the importance of recognizing key support and resistance levels but also how to capitalize on trend shifts and potential breakout points.
The Blue Jacket Competition:
The Blue Jacket competition is an ideal platform for traders to apply their Market Profile knowledge. Traders who integrate Market Profile analysis into their strategies can effectively identify trend shifts, anticipate breakouts, and manage risk.
The examples on the Bookmap Insights page dated June 19, June 11, and April 17 showcase how traders have used Market Profile to gain an edge in the competition.
Understanding market profile trading empowers participants in trading competitions with a distinctive advantage. The Blue Jacket competition exemplifies how market profile proficiency can elevate both individual traders and the broader trading community.
Ready to showcase your understanding of Market Profile Trading? Use your unique trading insights and strategies to inspire the Bookmap community. Your journey to becoming a trading leader starts here. Step into the Blue Jacket competition today.
Conclusion on Market Profile Trading
In conclusion, Market Profile is a powerful tool for dissecting market behavior, centering on the relationship between price, volume, and time. Its primary components are Time Price Opportunities (TPOs), which highlight specific price ranges over periods; the Value Area, denoting the commonly accepted price range; and the Point of Control (POC), marking a balance between buyers and sellers. This method equips traders with the skills to spot trends, manage risks, and understand market sentiment.
When applied to trading competitions, especially ones like the Blue Jacket competition, knowledge of Market Profile offers participants a significant advantage, enabling them to craft well-informed trading strategies.
Optimize your market profile trading with Bookmap. Sign up now for FREE.

Market Profile Trading is more than just another tool in financial analysis; it’s a game-changer. From a unique approach to understanding markets, it’s now a must-know for top traders.
In this guide, we’ll break down the essentials of Market Profile, explore how traders use it in real-world situations, and even see its power in action in the Blue Jacket competition. Ready to dive deep and level up your trading? Let’s get started.
What is Market Profile Trading?
Market profile trading examines financial markets by offering a unique perspective on market behavior. It focuses on the relationship between price, volume, and time.
It provides traders and investors with insights into the market’s:
Structure
Price distribution, and
Trading activity happening over a specific period.
Developed by J. Peter Steidlmayer in the 1980s, Market profile trading has since gained popularity among both institutional and retail traders for its ability to offer a deeper understanding of market dynamics.
Market profile trading organizes price and volume data in a graphical format called a “market profile chart,” which displays the market’s price distribution over time. This chart helps traders identify areas of strong and weak demand, as well as potential price levels where significant trading activity is concentrated.
The Three Building Blocks of Market Profile Trading
Market profile trading is a methodology that focuses on three fundamental building blocks or elements, which are:

| The Element: | What does it represent? | Practical Use: | What insights do traders gain? |
| Time Price Opportunities (TPOs) | TPOs are vertical bars, or “brackets” that represent a specific price range traded during a given period. | A cluster of TPOs around a particular price level indicates that traders are actively participating and transacting at that level. | This information helps traders identify:
a) Potential support and resistance levels, b) Entry and exit points, and c) Areas of price consolidation
|
| Value Area | It represents the price range within which approximately 70% of the trading volume occurred during a specified period. | If the current price moves outside the Value Area, it signals a potential trend continuation or reversal. | This information helps traders to spot emerging trends. |
| Point of Control (POC) | The point of control refers to the price level at which the highest volume of trading activity occurred during a specific period. | Case 1: If the POC is located near a support or resistance level, it can serve as a confirmation of the level’s significance.
Case 2: If the market moves away from the POC, traders might anticipate a potential trend in the direction of the movement. | Traders use the POC to identify levels of equilibrium between buyers and sellers. |
Must Read: Traders often merge data from TPOs, Value Area, and POC for comprehensive insights. For instance, if TPOs highlight accumulation near a pivotal support level inside the Value Area, and the POC corroborates high activity at the same level, traders might see this as a robust support zone, favoring long trades.
Volume Profile vs. Market Profile: Distinguishing the Two
Volume Profile and Market Profile, though often used interchangeably, have distinct methodologies in market analysis. Here’s a breakdown of both profiles:

Volume Profile:
- This approach focuses primarily on the vertical representation of trading volume at various price levels.
- It provides insights into areas of high and low trading activity and helps identify support and resistance levels.
- Volume Profile does not place as much emphasis on time-based analysis as Market Profile does.
Market Profile:
- Integrates both price and time, constructing TPOs to represent traded price ranges over specific intervals.
- Delivers a holistic understanding of market dynamics by mapping the relationship between price levels, volume, and time.
- Distinguishes itself through its time-centric approach, providing traders with a deeper insight into market structure.
For a clearer distinction, refer to the comparative table below:
Parameters | Volume Profile | Market Profile |
Focus | Primarily on trading volume | Focuses on price, time, and volume |
Representation | Vertical histogram | TPOs (vertical bars) |
Information | Shows volume at specific price levels | Depicts price ranges and time spent trading within those ranges |
Time Consideration | Less emphasis on time | Emphasizes time-based analysis |
Key Components | Volume at price levels (PVP, VAH, VAL) | TPOs, Value Area, Point of Control |
Interpretation | Identifies areas of high/low trading activity | Detects support/resistance levels, trend shifts, and gauges market sentiment |
Application | Effective for spotting support/ resistance levels and potential breakout zones | A comprehensive view of market dynamics, trend confirmation, and strategic trade setups |
Market Profile Trading Strategies
Market Profile Trading offers various strategies that cater to different market conditions, helping traders refine their decisions and improve outcomes. Here are some common strategies used by traders:
1. Value Area Trading
- Traders use the Value Area (where 70% of the trading volume occurs) to determine potential trading opportunities.
- Strategy: When the price re-enters the Value Area after breaking out, it often signals a potential reversal. Traders can use this information to plan long or short trades.
2. Support and Resistance Plays
- Identifying support and resistance levels from the Value Area boundaries or the Point of Control (POC) is a common strategy.
- Strategy: Traders might look for rejection at these levels, which could signal potential entry points with tight stop-losses.
3. Trend Following
- By observing the Value Area shifting higher or lower over time, traders can identify and confirm trends.
- Strategy: Enter trades in the direction of the trend, using the POC and TPO clusters for confirmation.
4. Breakout Trading
- Market Profile charts often reveal periods of consolidation followed by breakouts.
- Strategy: Traders monitor price action near the Value Area extremes. If the price breaks out and sustains above or below the extremes, it may signal a new trend.
By combining these strategies with other technical indicators, traders can increase their odds of success and better manage risks in dynamic market environments.
How Does Market Profile Trading Guide Trading Decisions?
Market profile trading guides trading decisions by providing traders with valuable insights into market trends, risk management, and market sentiment. Here’s how traders use market profile to make informed choices:

Identifying Market Trends:
- Market Profile helps traders identify market trends by visually representing the distribution of trading activity and price levels.
- By observing the shape of the market profile chart, traders can interpret whether the market is in a trending phase, a consolidation phase, or a reversal.
- For example,
- In an up-trending market, the Value Area might be shifting higher, indicating higher demand and potential upward momentum.
- Conversely, a market profile with a wider range and more balanced distribution may indicate a consolidation phase.
Managing Risk:
- Market Profile aids in risk management by highlighting key support and resistance levels, as well as areas of high trading activity.
- Traders can use the value area and point of control to identify levels where the price is likely to find support or encounter resistance.
- This information can be crucial for setting stop-loss orders and profit targets.
Spot Market Sentiment:
- Market Profile provides insights into market sentiment by showing where most of the trading activity is concentrated.
- For example,
- If the point of control is positioned near the upper end of the Value Area, it suggests bullish sentiment.
- On the other hand, if the point of control is closer to the lower end of the Value Area, it may indicate bearish sentiment.
Additionally, observing the shape of the TPOs can also indicate whether the majority of traders are buying or selling at specific price levels, helping traders fine-tune their strategies based on prevailing market sentiments.
Market Profile Charts
A Market Profile Chart is the cornerstone of Market Profile Trading, visually representing the distribution of trading activity across price and time. Understanding its components is essential for leveraging its full potential.
Key Features of Market Profile Charts:
- Time Price Opportunities (TPOs):
- Represented by letters or brackets, TPOs display price levels traded during specific time intervals.
- A dense cluster of TPOs indicates significant market activity at that price.
- Value Area:
- The Value Area highlights the price range where most of the trading volume occurred.
- It serves as a benchmark for identifying support, resistance, and potential breakout zones.
- Point of Control (POC):
- The POC is the price level with the highest trading activity.
- It acts as a balance point, often indicating equilibrium between buyers and sellers.
How to Interpret Market Profile Charts:
- Trending Markets: A progressive shift in the Value Area and POC indicates a trending market.
- Consolidation Phases: A balanced profile with TPOs concentrated in the middle signals consolidation.
- Breakouts: Price movement away from the Value Area extremes often leads to breakouts, creating trading opportunities.
Benefits of Market Profile Charts:
- Enhanced Market Understanding: Gain insights into market structure and dynamics.
- Precision in Trade Entries and Exits: Use key levels such as the Value Area and POC to refine decisions.
- Improved Risk Management: Set more accurate stop-loss and profit targets by analyzing trading volume and price distribution.
Market Profile Charts provide a structured and intuitive way for traders to interpret complex market data, offering a significant edge in both day-to-day trading and competitive environments.
Practical Applications of Market Profile Trading
Traders use market profile trading to identify strategic trade setups like:
- Poor Highs/Lows,
- Determine support and Resistance levels
- Differentiate between consolidation and breakout periods, and
- Confirm trends
By incorporating these insights into their trading decisions, traders aim to enhance decision-making and increase their probabilities of success. Here are some practical applications of market profile trading:
1. Strategic Trade Setups:
- Traders use Market Profiles to devise strategic trade setups based on the insights gained from the distribution of trading activity.
- For example,
- A trader might identify a “Poor High” or “Poor Low” formation on the market profile chart.
- This occurs when the market makes a brief excursion beyond the previous day’s high or low but fails to sustain that level and returns within the Value Area.
- This setup could signal a potential reversal, prompting the trader to enter a trade with the expectation that the market will reverse its direction.
2. Support and Resistance Levels:
- Market Profile helps traders identify support and resistance levels with greater precision.
- Additionally, the upper and lower boundaries of the value area serve as potential areas where prices might reverse.
- By aligning these levels with other technical indicators, traders can make more informed decisions about placing stop-loss and take-profit orders.
3. Periods of Consolidation and Breakout:
Market profile assists traders in distinguishing between periods of consolidation and potential breakout scenarios in the following manner:
Aspects | Consolidation | Breakout Opportunities |
Indicator | During consolidation, the Value Area narrows, reflecting a lack of directional movement. | If the market profile shows a wide Value Area with price acceptance at the extremes, it suggests potential breakout opportunities.
|
Trader’s Action | Traders consider range-bound strategies, such as mean reversion techniques, within these periods. | Traders can prepare for breakout trades by monitoring the price’s reaction as it approaches the Value Area boundaries. |
4. Trend Identification and Confirmation:
- Traders utilize market profiles to confirm or identify emerging trends.
- If the market profile consistently shows a one-sided distribution of TPOs and the point of control shifts in the direction of the trend, it suggests a strong and sustained trend.
The Competitive Advantage: Market Profile in Trading Competitions

In the world of trading competitions, having a deep understanding of tools like the Market Profile can provide participants with an unparalleled edge. For instance, in one of the Blue Jacket competitions, a participant showcased their proficiency with Market Profile by analyzing the intricate relationship between price, time, and volume. View insights into market profile here.

They then presented a meticulous trading strategy backed by insightful screenshots and videos, explaining their moves every step of the way. This strategy not only highlighted the importance of recognizing key support and resistance levels but also how to capitalize on trend shifts and potential breakout points.
The Blue Jacket Competition:
The Blue Jacket competition is an ideal platform for traders to apply their Market Profile knowledge. Traders who integrate Market Profile analysis into their strategies can effectively identify trend shifts, anticipate breakouts, and manage risk.
The examples on the Bookmap Insights page dated June 19, June 11, and April 17 showcase how traders have used Market Profile to gain an edge in the competition.
Understanding market profile trading empowers participants in trading competitions with a distinctive advantage. The Blue Jacket competition exemplifies how market profile proficiency can elevate both individual traders and the broader trading community.
Ready to showcase your understanding of Market Profile Trading? Use your unique trading insights and strategies to inspire the Bookmap community. Your journey to becoming a trading leader starts here. Step into the Blue Jacket competition today.
Conclusion on Market Profile Trading
In conclusion, Market Profile is a powerful tool for dissecting market behavior, centering on the relationship between price, volume, and time. Its primary components are Time Price Opportunities (TPOs), which highlight specific price ranges over periods; the Value Area, denoting the commonly accepted price range; and the Point of Control (POC), marking a balance between buyers and sellers. This method equips traders with the skills to spot trends, manage risks, and understand market sentiment.
When applied to trading competitions, especially ones like the Blue Jacket competition, knowledge of Market Profile offers participants a significant advantage, enabling them to craft well-informed trading strategies.
Optimize your market profile trading with Bookmap. Sign up now for FREE.
 Twitter
Twitter
 Facebook
Facebook