Wyckoff Trading Strategy: Understanding the Wyckoff Market Cycle
Financial markets move in patterns. These patterns don’t just appear randomly; they emerge after some specific and predictable events. Richard D. Wyckoff, in the early 20th century, identified these patterns and developed a powerful trading strategy known as the Wyckoff Method. This method helps traders understand and predict stock market movements by focusing on market cycles and price patterns. It breaks down stock price behavior into four distinct phases: accumulation, markup, distribution, and markdown.
In this article, we will explore each phase in detail. We’ll start with the accumulation phase, where smart investors buy shares at lower prices. Next is the markup phase, where prices begin to rise as these investors sell their shares. Then, we’ll cover the distribution, where the stock price moves sideways as smart money sells at higher levels. Finally, we’ll examine the markdown phase, where prices decline due to increased selling pressure.
Moreover, you’ll also discover how to apply the Wyckoff Method using real-world examples and strategies for entering and exiting trades. Lastly, we’ll show you how integrating tools like Bookmap can enhance your analysis by providing real-time insights into market liquidity and order flow. This combination will help you make more informed trading decisions and improve your overall trading strategy. Let’s get started.
What is the Wyckoff Method?
The Wyckoff Method is a technique used in technical analysis. It is used to study and predict stock market movements. This method focuses on understanding market cycles and price patterns to make better trading decisions. Developed by Richard D. Wyckoff in the early 20th century, this method helps traders identify the best times to buy and sell stocks by analyzing the behavior of big market players.
The Wyckoff Method is usually divided into four different phases:
| Phases | Action of market participants | Impact on stock prices |
| Accumulation |
|
|
| Markup |
|
|
| Distribution |
|
|
| Markdown |
|
|
For more clarity, let’s study an example of a stock moving through these phases:
Let’s take a hypothetical stock, XYZ Corp., to illustrate these phases:
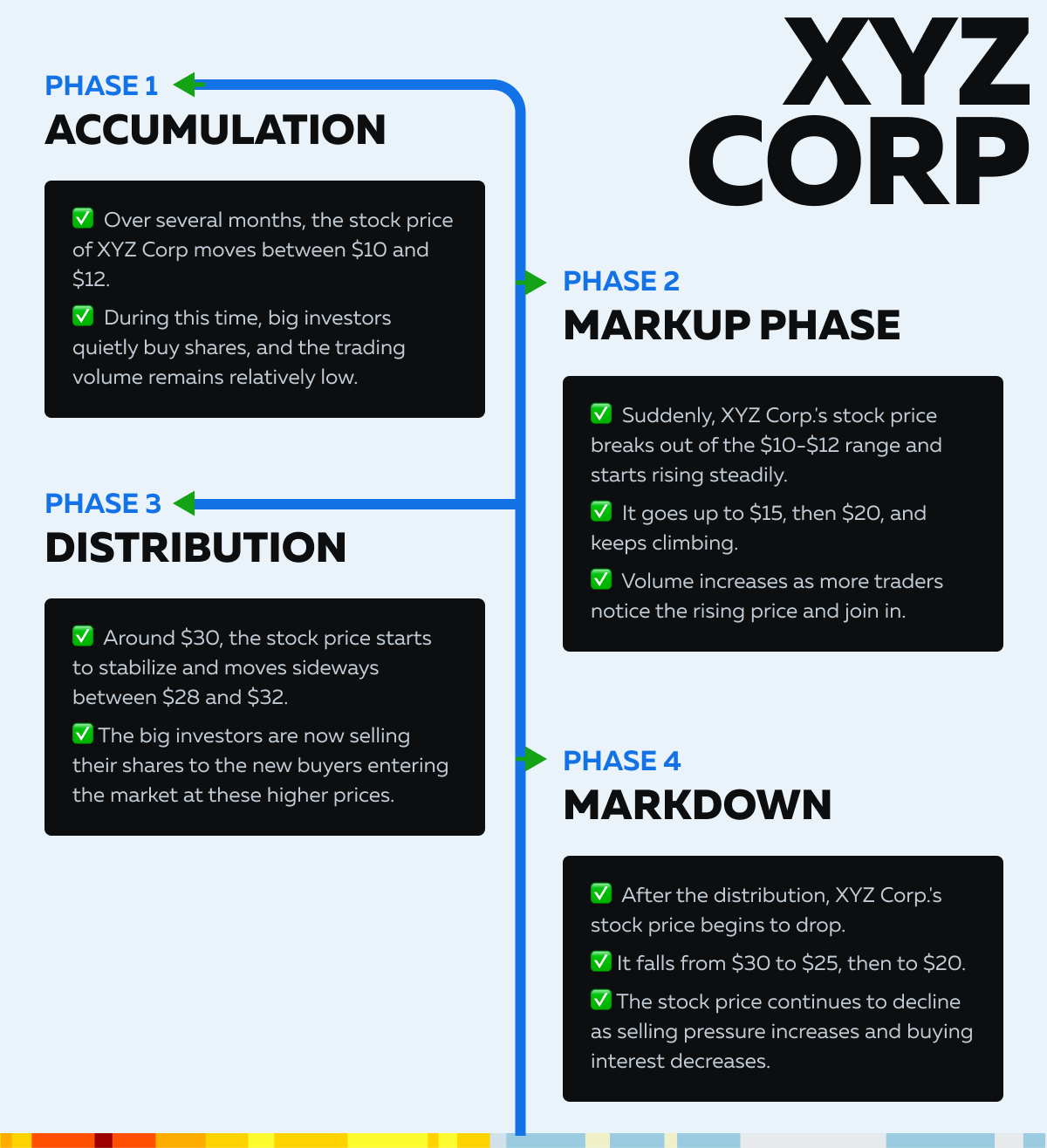
Now, let’s study these four phases in detail and learn how to identify them. Also, we will check how to make appropriate strategies for each phase.
Wyckoff Accumulation Phase
The accumulation phase is a period in the market cycle where smart money (large, informed investors) quietly buys shares at lower prices before a major uptrend. During this phase, the stock price moves within a relatively narrow range. Such a movement is an indication that the big players are building their positions without causing significant price increases.
How to Identify Accumulation Phases?
Traders can identify accumulation phases by analyzing the following:
| Volume | Price Patterns | Market Sentiment |
|
|
|
Chart Example (Showing High Volume and Strong Support Levels)
For more clarity, let’s have a look at the below chart showing how a stock might look during the accumulation phase:

Please note that:
- $10.0 is the initial support level, with high buying interest.
- $12.0 represents the second support level where accumulation is evident.
- $13.0 further indicates a strong support level where the price consistently finds buying interest.
What are the Strategies for Entering Trades During Accumulation?
- Look for confirmation that support levels are holding strong.
- When the price bounces off support levels with high volume, it signals that accumulation is taking place.
- Place stop-loss orders just below the key support levels to manage risk.
- This protects your investment if the price breaks below the support, indicating a potential failure of the accumulation phase.
- Instead of buying all at once, consider accumulating shares gradually as the price moves within the range. This approach mirrors the smart money strategy and reduces the risk of price manipulation.
How to Set Buy Orders at Key Support Levels?
Let’s understand in some simple steps:
Step I: Identify Key Support Levels
- Use historical price data to identify where the stock has consistently found support.
- Say $10 and $12 are key support levels.
Step II: Set Buy Orders
- Place buy orders slightly above these support levels.
- For example, you might set a buy order at $10.50 if $10 is the identified support level.
- This ensures you enter the trade as the price approaches the support, but don’t miss out if the price doesn’t reach exactly $10.
Step III: Monitor Volume
- Ensure that buy orders are supported by high volume on up days.
- High volume confirms that smart money is buying and indicates a stronger accumulation phase.
Markup Period
The markup period is the phase in the market cycle that follows the accumulation phase. During this time, the stock price starts to rise steadily. This increase in stock price happens as the smart money begins to sell its accumulated shares to the broader market.

How to Spot the Beginning of a Markup Period?
Traders can identify the start of a markup period by looking for:
| Price Breakouts | Increasing Volume |
|
|
Chart Example (Showing Increased Buying Pressure and Upward Movement)
For more clarity, let’s have a look at the below chart showing how a stock might look during the markup phase:

Please note that the resistance level is at $20. Once it is crossed, the price breaks above it with increased volume.
How to Capitalize on the Markup Period?
- Once the markup phase begins, consider buying shares and holding them to ride the trend upward.
- Use technical indicators like moving averages (e.g., 50-day or 200-day) to confirm the trend direction.
- Set trailing stops to protect profits while allowing the stock price to continue rising.
- Keep an eye on volume trends. Increasing volume confirms the strength of the markup.
- Look for days with high volume, as they indicate strong buying interest.
How to Monitor Liquidity Zones and Adjust Positions?
For the unaware, liquidity zones are areas where there is a significant amount of buy and sell orders. These zones often act as support or resistance levels during the markup phase. Use historical price data to identify these zones. Now, as the markup progresses, adjust your positions based on the stock’s performance and market conditions.
For example:
- Add to Positions: If the stock breaks new highs with strong volume, consider adding to your position.
- Take Profits: When the stock reaches key resistance levels or shows signs of weakening (e.g., decreasing volume, lower highs), consider taking partial profits or setting stop-loss orders to protect gains.
- Stay Informed:
- Continuously monitor:
- News
- Earnings reports, and
- Market sentiment
- These factors significantly impact the markup phase
- Also, stay updated with technical analysis tools and indicators to make informed decisions.
- Continuously monitor:
Distribution Phase
The distribution phase is the period in the market cycle where smart money (large, informed investors) begins to sell off their shares at higher prices after the markup phase. During this phase, the stock price moves within a relatively narrow range. This situation indicates that big investors are distributing their holdings to the broader market. Often, this phase leads to increased volatility and signals the start of a downtrend.
How to Identify Distribution?
Traders can identify the distribution phase by looking for:
| Selling Pressure | Resistance Levels |
|
|
Chart Example (Showing High Volume at Resistance Levels)
For more clarity, let’s have a look at the below chart showing how a stock might look during the distribution phase:
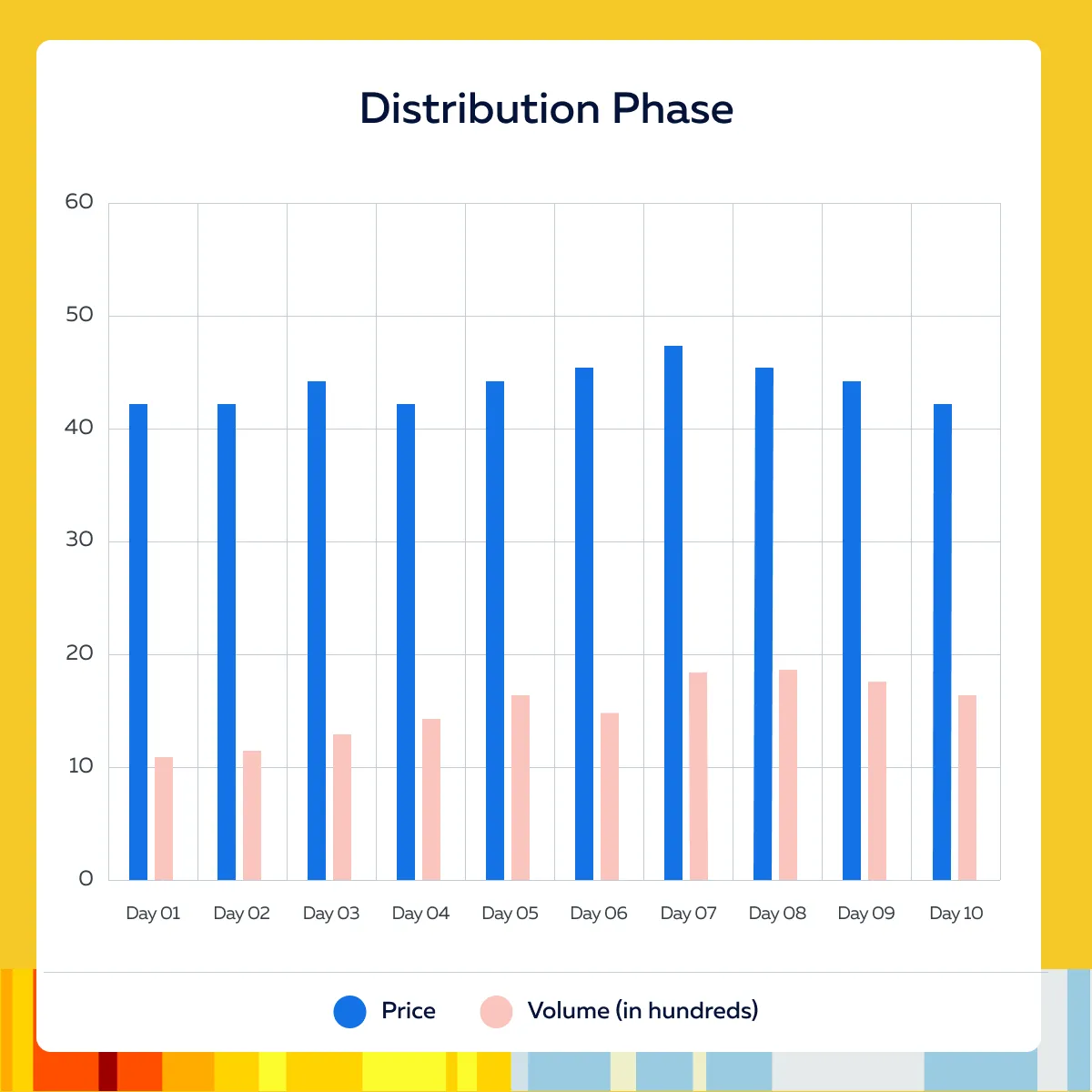
Please note that the resistance levels are visible at $44, $46, and $48.
How to Exit Positions or Do Short Selling?
As signs of distribution become apparent, consider gradually exiting your positions. Sell shares incrementally to:
- Avoid causing significant price drops
and
- To take advantage of remaining buying interest.
Furthermore, look for opportunities to short-sell the stock. Short selling involves borrowing shares to sell at current prices and buying them back at lower prices once the stock declines. Also, monitor the volume closely. Increasing volume on down days compared to up days indicates stronger selling pressure. This is usually one of the best cues to exit long positions or enter short positions.
How to Set Sell Orders at Resistance Levels and Identify Short-Selling Opportunities?
Follow these simple steps:
Step I: Identify Resistance Levels
- Use historical price data and recent trading activity to identify key resistance levels where the stock has struggled to move higher.
- In the above chart, $46-$48 is a key resistance zone.
Step II: Set Sell Orders
- Now, place sell orders slightly below resistance levels to ensure you can exit before the price potentially falls.
- For example, if $48 is a resistance level, consider setting a sell order at $47.50.
Step III: Identify Short-Selling Opportunities
| Breakdown Below Support | Bearish Patterns |
|
|
Step IV: Risk Management
- Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on short positions.
- Set stop-loss orders just above key resistance levels to protect against unexpected price increases.
Markdown Period
The markdown period is the phase in the market cycle that follows the distribution phase. During this period, the stock price moves downward as selling pressure outweighs buying interest. This phase is characterized by declining prices, lower highs, and lower lows and can lead to significant losses if not managed properly.
How to Identify the Start of a Markdown Period?
Traders can identify the start of a markdown period by looking for:
| Declining Volume | Price Breakdowns |
|
|
Chart Example (Showing Increased Selling Pressure and Downward Movement)
For more clarity, let’s have a look at the below chart showing how a stock might look during the markdown phase:
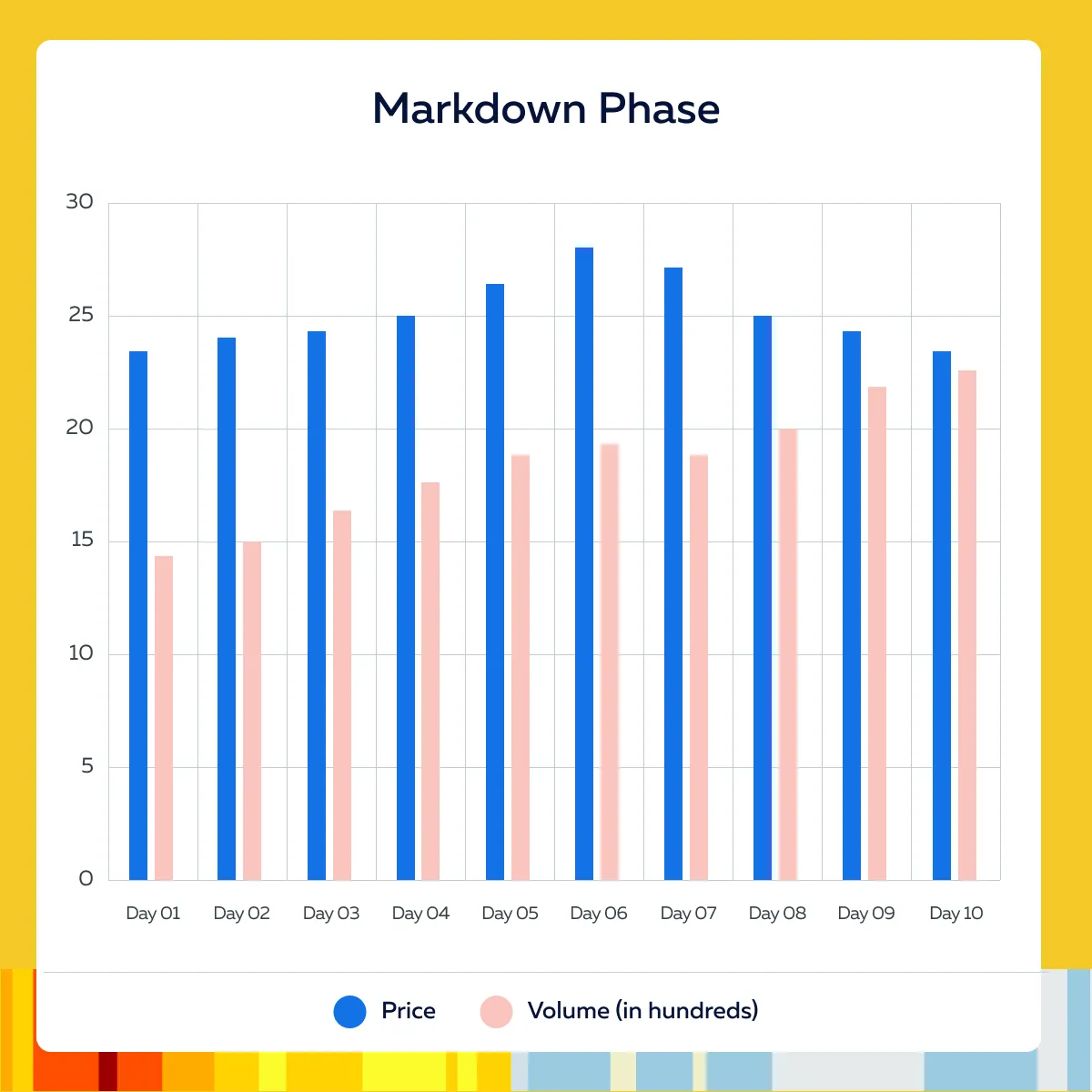
Please note that the stock price breaks below the $26 support level with increased selling pressure. This is an indication of the start of the markdown phase.
How to Capitalize on the Markdown Period?
- Short Selling:
- Short selling involves borrowing shares to sell at current prices, to buy them back at lower prices.
- This strategy allows traders to profit from declining prices.
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders:
- Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on short positions.
- Set stop-loss orders above key resistance levels to protect against unexpected price increases.
- Volume Analysis:
- Monitor volume trends closely.
- A decrease in volume on up days and an increase on down days confirms strong selling pressure.
How to Monitor Price Movements and Adjust Short Positions?
Use historical price data and recent trading activity to identify key support levels where the stock may temporarily stabilize and resistance levels where it may encounter selling pressure. Now, you can adjust positions by:
- Adding to Short Positions: If the stock breaks below new support levels with strong selling pressure, consider adding to your short position.
- Covering Short Positions: If the stock shows signs of stabilizing or reversing (e.g., decreasing selling volume, forming a base), consider covering (buying back) your short positions to lock in profits.
Moreover, prefer using technical indicators to gauge the strength and duration of the markdown phase. Some common examples include:
- Relative Strength Index (RSI)
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
- Trendlines
Integrating Wyckoff for Improved Trading
Be aware that integrating the Wyckoff method with other analytical tools can significantly:
- Enhance market analysis
and
- Improve trading decisions
One such tool is Bookmap. Being a modern analytical tool, it provides advanced visualization of market data through heatmaps and order flow analysis. By combining Wyckoff’s market cycle analysis with Bookmap’s real-time data, you can gain a more comprehensive understanding of market phases and trader behavior. Also, such combined usage can improve the accuracy of your trading strategies.
How Bookmap Enhances Wyckoff Analysis?
| Heatmap Visualization | Order Flow Data |
|
|
For more clarity, let’s study a hypothetical example confirming Wyckoff patterns with Bookmap.
- Say a trader identifies a potential accumulation phase based on Wyckoff’s principles.
- They note the stock’s price range and low volume during the consolidation period.
- Now, the trader uses Bookmap’s heatmap to look for:
- High buying interest
and
- Minimal selling pressure around the key support levels identified by Wyckoff.
- The trader monitors the order flow data and spots large buy orders (icebergs) at support levels.
- This situation confirms the presence of strong buying interest.
Real-Time Validation of an Accumulation Phase Using Bookmap
To better understand the usage of Bookmap as an advanced analytics tool, let’s study another example. Say, using Wyckoff’s method, the trader identifies that XYZ Corp. is in the accumulation phase, with the price moving sideways between $40 and $42.
Now, the trader switches to Bookmap to confirm this phase in real time. They performed the following steps:
- Setup on Bookmap:
- Heatmap Display: The trader sets up Bookmap’s heatmap to monitor the order book for around $40.
- Order Flow Monitoring: The trader watches for large buy orders appearing at $40, with minimal sell orders (this validates the accumulation phase).
- Real-Time Observation:
- High Buying Interest: The heatmap shows a cluster of large buy orders at $40, with very few sell orders (this indicates strong buying interest).
- Order Flow Confirmation: Order flow data reveals large icebergs at $40, with minimal activity from sellers (this confirms the Wyckoff accumulation phase).
- Entry Decision:
- Confirming Wyckoff Patterns: The trader decides to enter a long position at $40 by placing buy orders just above the support level.
- Setting Stop-Loss: A stop-loss is placed below the next support level to ensure protection against potential breakdowns.
Conclusion
The Wyckoff trading strategy is a popular technique for understanding market movements through four distinct phases: accumulation, markup, distribution, and markdown. During the accumulation phase, smart money buys shares at lower prices and sets the stage for a markup period where prices rise. Next comes the distribution phase, in which shares are sold off at higher prices. This sell-off leads to a markdown phase where prices decline.
By combining the Wyckoff method with tools like Bookmap, traders can significantly enhance their trading strategies. Bookmap provides real-time insights into market liquidity and order flow through heatmap visualizations and the most recent order flow data. These Bookmap’s features help to confirm Wyckoff patterns and gain a clearer picture of market trends.
Sign up for FREE to Bookmap today and significantly improve the accuracy of your trading strategies.

 Twitter
Twitter
 Facebook
Facebook